Asia
To which language should you translate to localize in China?
What we know from our community
“There are a variety of languages being spoken in Mainland China, and mandarin was considered as
the national language by the early 20th century. As a way to encourage literacy, simplified Chinese
characters have been brought to use since the 1950s. Along with traditional Chinese characters
(which are still used in Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan), they are two standard character sets of the
contemporary Chinese written language.
Not like many other languages, in Chinese, the writing system and the spoken language aren’t
interlinked. Furthermore, Chinese has no verb tenses, no distinction between singular and plural, and
no alphabet. There are several dialect groups in Chinese, the differences between these dialects can
be so huge which make some of them almost indistinguishable from each other. However, as the
language is not phonetic, the Chinese characters can be used to write both Mandarin and the
dialects.Chinese speakers represent an exciting market opportunity, thus localizing to Chinese is very
important. Yet it can be very tricky without a good understanding of the culture and the market.”
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Chinese (92%)
Actual languages
Chinese (92%), Zhuang (1.4%), Hui (0.8%), Yi (0.6%), Uighur (0.6%), Tujia (0.5%), Tibetan (0.4%), Mongolian (0.2%), Korean (0.1%), other (3.4%)
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in China
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 106/150 localize by translating into Simplified Chinese
- 8/150 localize by translating into Chinese
- 5/150 localize by translating into Traditional Chinese
- 7/150 localize by translating into both Simplified Chinese and Traditional Chinese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into both Simplified Chinese and French
- 1/150 localizes by translating into both Simplified Chinese and Hmong language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Korean, Chinese (Fuzhounese), Chinese (Hainanese), Chinese (Shanghainese), Chinese (Sichuanese), Chinese (Wenzhounese), Chinese (Yunnanese), Chinese Cantonese (Simplified), Chinese Cantonese (Traditional), Chinese Mandarin (Simplified), Chinese Mandarin (Traditional) and Chinese Sign Language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Simplified Chinese, Portuguese, German, Korean and Japanese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Portuguese, German, French, Japanese, Spanish, Italian, Bahasa Indonesia, Hungarian, Polish, Romanian, Turkish, Russian, Thai and Ukrainian
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Overview
Language
Official language
Mandarin – up to 70% of the population can speak Mandarin.
T-index
11.3%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
Other languages
Standard Mandarin, Cantonese (Hong Kong and Macau), Portuguese (Macau), English (Hong Kong), Mongolian (Inner Mongolia, Haixi in Qinghai, Bayingolin and Bortala in Xinjiang), Korean (Yanbian in Jilin), Tibetan (Tibet, Qinghai), Uyghur (Xinjiang), Zhuang (Guangxi, Wenshan in Yunnan), Kazakh (Ili in Xinjiang), Yi (Liangshan in Sichuan, Chuxiong and Honghe in Yunnan)
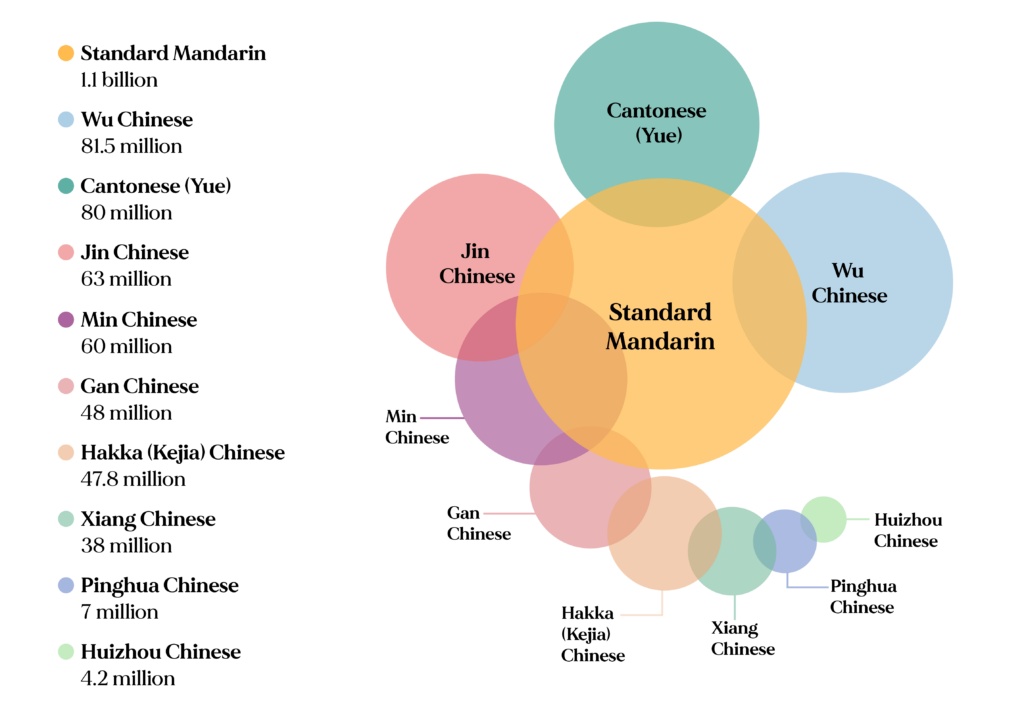
Cantonese is used as the official language in Hong Kong, as envisaged by the Hong Kong Basic Law, and is used in all government communication, including court and tribunal proceedings. Cantonese is also the official language in Macau, along with Portuguese. The use of Cantonese in Hong Kong is regulated by the Official Language Division of the Civil Service Bureau, a government institution. In Macau, the use of the language is regulated by the Public Administration and Civil Service Bureau. According to linguists, Cantonese is defined as a variant of the Chinese language or as a prestige variant of Yue, a subdivision of Chinese. When classified with other closely related Yuehai dialects, Cantonese has about 80 million speakers across the country. In the Guangzhou province, Cantonese is used as the lingua franca as well as in the neighbouring region of Guangxi. Cantonese can be divided into three main dialects: the Guangzhou dialect, Hong Kong dialect, and Macau dialect. All of these dialects are geographically defined.
English
Low proficiency (EF) – 62 of 111 countries/regions in the world- 8/24 position in Asia.
English is one of the most important foreign languages in China, with about 10 million speakers all over the country. The majority of English speakers are found in the urban centres of the country. In Hong Kong, English is established as an official language and is used in both print and electronic media. English is also used as a lingua franca in China during international engagements.
Most studied languages
There have been a growing number of students studying Arabic for reasons of cultural interest and belief in better job opportunities. The language is also widely studied amongst the Hui people. In the past, literary Arabic education was promoted in Islamic schools by the Kuomintang when it ruled mainland China.
There have also been a growing number of students choosing to learn Urdu, due to interest in Pakistani culture, close ties between the respective nations, and job opportunities provided by the CPEC.Interest in Portuguese and Spanish has increased greatly, due in part to Chinese investment in Latin America as well as in African nations such as Angola, Mozambique, and Cape Verde. Portuguese is also one of the official languages in Macau, although its use had stagnated since the nation’s transfer from Portugal to the PRC.
Demography
Capital: Beijing
Currency: Renminbi
Population: 1 412 bilion
Population density: 150/km2
Economy
GDP: 17,963,170.52 million USD (2022)
GDP per capita: 12,720.2 USD (2022)
Exports: $3.34 Trillion (2021)
Statistics
Internet users: 73.7% penetration, 1.05 billion
Unemployment rate: 4.9% (2022)
Urbanisation: 64% (2022)
Literacy: 97% (2020)
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numbering system, point as decimal separator and space or comma as separator of thousands.
Date format: yyyy-mm-dd
Time: 24h time system
Country code: 0086
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal
Facts and data
Economy
Imports
$1.97 trillion (2021). Crude Petroleum ($208B), Integrated Circuits ($171B), Iron Ore ($146B), Petroleum Gas ($56.6B), and Copper Ore ($52.4B), importing mostly from South Korea ($158B), Japan ($153B), United States ($151B), Australia ($138B), and Chinese Taipei ($126B).
In 2021, China was the world’s biggest importer of Crude Petroleum ($208B), Iron Ore ($146B), Petroleum Gas ($56.6B), Copper Ore ($52.4B), and Soybeans ($44.2B).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 88.7% have an account with a financial institution
• 38% have a credit card
• 71.2% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
Very Easy to conduct business (77.9 out of 100) 6th out of 25 Asia Pacific countries, 31st worldwide out of 190 countries (2022, World Bank).
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 3rd out of 17 South East Asia, East Asia and Oceania countries, 11th out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Exports
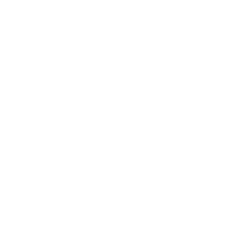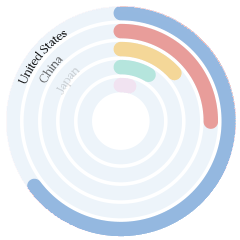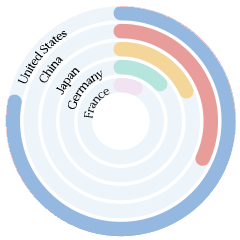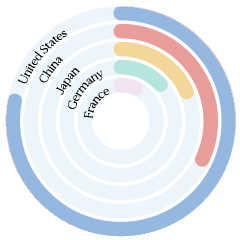
$3.34 trillion (2021). Broadcasting Equipment ($231B), Computers ($192B), Integrated Circuits ($158B), Office Machine Parts ($101B), and Telephones ($53.9B), exporting mostly to United States ($530B), Hong Kong ($323B), Japan ($168B), South Korea ($140B), and Germany ($134B).
In 2021, China was the world’s biggest exporter of Broadcasting Equipment ($231B), Computers ($192B), Office Machine Parts ($101B), Telephones ($53.9B), and Semiconductor Devices ($49.2B).
Main local online stores
Taobao.com, Tmall.com, 360buy.com, Suning & Gome, QQ buy, Dangdang, Vancl, 51buy& Coo8, Yihaodian, Meituan & 55 tuan, Dianping, Taobao Juhuasuan, Mbaobao, Redbaby, Jiuxian, La Miu, VipShop, FClub, Meilishuo, eTao.
Economic freedom
‘Mostly not free’ (48.3 out of 100) 34th out of 39 countries in Asia Pacific 154th worldwide out of 176 countries (2022, Heritage Foundation and Wall Street Journal).
Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal
Service Imports (2020)
Service Exports (2020)
Source: OEC
Historical Data Trade Imports
The following section uses historical trade data imports from partners of China.
Historical Data Trade Exports
The following section uses historical trade data exports from partners of China.
Source: OEC
China's Most Specialized Products
Specialization is measured using Revealed Comparative Advantage (RCA), an index that takes the ratio between China observed and expected exports in each product.
Source: OEC
Market Growth Imports (2020)
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start importing that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Market Growth Exports (2020)
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start exporting that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Source: OEC
Preferred payment methods among Chinese millionaires as of 2018
China's most popular digital payment services (%)
Source: Human Research Institute
Source: Statista Tech Giants 2019
T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media language Chinese, English
Information channels
China is the largest media market in the world, and has the world’s largest online population. Outlets operate under tight Communist Party control. The opening-up of the industry has extended to distribution and advertising, not to editorial content. However, there is leeway for independent coverage that is not perceived as a threat to social stability or the Party. Reporters Without Borders (RSF) has described President Xi Jinping as the “planet’s leading censor and press freedom predator” describing government policies as aimed at achieving “complete hegemony over news coverage and the creation of an international media order heavily influenced by China”. Beijing tries to limit access to foreign news by restricting rebroadcasting and the use of satellite receivers, by jamming shortwave broadcasts, including those of the BBC, and by blocking websites. Overseas Chinese-language news outlets that are not state-owned are blocked in mainland China. However, international English language websites like the BBC are often available to view although content that is contrary to Communist Party rhetoric is filtered and English-language news sites can be filtered at times of tension. Fears that the media in Hong Kong would lose its independence when the territory reverted to Chinese control in 1997 have generally not been borne out. Hong Kong still has editorially-dynamic media, but worries about interference remain. TV is available in most homes and the sector is competitive, especially in cities. There are more than 3,300 local, regional and national TV channels. State-run Chinese Central TV (CCTV) is China’s largest media company. Its dominance is challenged by provincial TVs, which are on the air nationally via satellite. China is a major market for pay TV, which is almost entirely delivered by cable. All of China’s 2,600-plus radio stations are state-owned. There are around 1,900 newspapers. Each city has its own title, usually published by the local government, as well as a local Communist Party daily. China spends hugely on TV, radio, online and press outlets targeted at international audiences, aiming to extend its political influence and boost its image. It is less keen to allow foreign players into the domestic market. Phenomenal online growth Around 26.7% of the online population live in rural areas. According to CNNIC, 98.6% of China’s online population can access the internet via a smartphone. There are three powerful online giants, known collectively as “BAT”: Baidu is the top search engine; e-commerce leader Alibaba has allied with Sina, which operates the Weibo microblog platform; and Tencent owns instant messenger WeChat. Because of official censorship, Weibo is losing some of its appeal as a forum where relatively uncensored news can be shared. WeChat, Tencent’s take on the WhatsApp instant messenger, has the largest number of domestic users of any social media service in China. China has the world’s largest online video market. Streaming platforms, including market leader iQiyi, Youku Tudou and Sohu have a huge following and pose a challenge to traditional TV. An extensive web filtering system, dubbed the “Great Firewall of China”, blocks tens of thousands of sites using URL filtering and keyword censoring. Thousands of cyber-police watch the web and material deemed politically and socially sensitive is filtered. Blocked resources include Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and human rights sites. The use of circumvention tools, including virtual private networks (VPNs), became harder after China strengthened its firewall to allow it to intercept data traffic to and from individual IP addresses. This was coined the “Great Fire Cannon” when it came into effect in 2015. The government since has signalled that it will ban unapproved VPNs.
The press
People’s Daily (Renmin Ribao) – Communist Party daily, web pages in English
China Youth Daily (Zhongguo Qingnian Bao) – state-run, linked to Communist Youth League
China Daily – official English-language paper
Global Times (Huanqiu Shibao) – state-run, editions in English and Chinese, focuses on world affairs
People’s Liberation Army Daily (Jiefangjun Bao) – web pages in English
Reference News (Cankao Xiaoxi) – published by official news agency Xinhua
21st Century (21 Jingji) – leading business newspaper, privately-owned
Television
Chinese Central TV (CCTV) – state-run national broadcaster; 18 free-to-air networks
China Global TV Network (CGTN) – state-run international broadcaster; networks in English, Arabic, French, Russian, Spanish
Radio
China National Radio – state-run
China Radio International – state-run external broadcaster, programmes in more than 40 languages, notably to Taiwan and Korea
News agency
Xinhua (New China News Agency) – state-run, web pages in English
China News Service (CNS) – state-run, web pages in English
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
73.7% penetration, 1.05 billion
Share of web traffic by device
53.72% mobile phones, 45.38% computers (laptops and desktops), 0.90% tablet devices.
Average speed of mobile Internet connection
109.40 Mbps
Average speed of fixed Internet connection
214.58 Mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population: 118.6%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G): 99.6%
Most popular web search engines
Baidu (60.47%), Bing (15.24%), Sogou (10.31%), Haosou (5.55 %), Google (3.26%), other (5.17%).
Most used social media
Facebook (60.04%), Twitter (19.33%), Pinterest (7.28%), YouTube (7.15%), Instagram (2.34%), Sina Weibo (1.46%) VKontakte (0.81%), other (1.58%).
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Number of internet users in China from 2009 to 2019, by connection type
(in millions)
Number of internet users in China as of March 2020, by activity
(in millions)
Source: MIIT
Source: CNNIC
Distribution of search engines users in China as of June 2019, by urban and rural area
Distribution of search engine users in China as of June 2019, by age group
Source: CNNIC
Average daily time spent consuming and interacting with media by the internet users in China between second quarter and third quarter 2018, by type
Sorces: GlobalWebIndex; WeAreSocial; Hootsuite
Social statistics
Life expectancy
78 yrs (2021)
Current health expenditure
5.59% of GDP
Current education expenditure
88.5% of total expenditure in public institutions
CO2 emissions
7.8 metric tons per capita
Cultural Curiosities
It is customary in the Chinese tradition to refuse gifts at least one time before accepting it, so do not react badly if your gifts are rejected at first.
When at the table it is considered a sign of appreciation of the food to burp after eating. Moreover, when at a restaurant it is impolite to leave a tip to the waiter. Lastly, Chinese people regard it as normal to spit on the streets and sometimes even indoors in public places such as buses or stations.
Corruption perceptions Index
China scored 45 out of 100, ranked 65th out of 180 countries worldwide.
World Happiness Index
China ranked 72nd out of 146 countries, with a score of 5.585.
Share of cities affected by acid rain
37.6%
Investment in pollution control
1.15 (% of GDP)
Use of Colors in China
Like in many countries, certain colors in China have scribed meanings. Red is the color of happiness, of positivity. For example when a baby is born the congratulations are often delivered in a red envelope. Historically, red was associated with fire. There is a Chinese saying “hóng hóng huǒ huǒ” which means the life of someone who grows, prospers, cracks and rockets like a red flame.
White also has a particular significance in the Chinese tradition, it is a color used to express sympathy in sad occasions. It must be avoided in celebratory occurrences such as weddings. It is a delicate color to use when conducting branding campaigns.
Yellow is a risky color to use when doing business in China, this color in publication and media is associated with pornographic material.
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
Where do people fail to attain a high school qualification?
% of 25-34 years old with an educational level below upper secondary in selected countries
Education struggling to keep up with digital advance
% who agree that their formal education has given them the technology knowledge they need
Source: OECD
Source: Dentsu Aegis Digital Society Index 2018
The countries with the most STEM graduates
Recent graduates in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (in the first decade of 2000)
Annual average of concentration of air pollutants of 338 cities in China in 2018
(in micrograms per cubic meter)
Source: World Economic Forum
Source: Ministry of Ecology and Environment
Share of total days of 337 cities in China based on level of pollution in 2019
Number of environmental incidents in China in 2019, by region
Source: Ministry of Ecology and Environment
Number of SmartHome forecast in China from 2017 to 2024
(in millions)
Forecasted investment value in smart city related technologies in China from 2018 to 2023
(in billion U.S dollars)
Source: IDC
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Languages research
Languages and dialects spoken in China
The geographical distribution of languages that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: Denys Nevozhai, Unsplash


