North America
To which language should you translate to localize in El Salvador?
What we know from our community
El Salvador, with an area of 20 thousand square kilometers, displays linguistic diversity. While Spanish is the dominant language, other pre-Columbian languages are spoken in specific communities. Salvadoran Spanish has unique characteristics, such as aspirating the final “s” and using diminutives, incorporating local expressions and regional vocabulary.
Indigenous communities work to preserve their ancestral languages. Nahuat, spoken in rural areas of Ahuachapán, Sonsonate, and La Libertad, was historically spoken by the Pipil people. The Pipil, culturally related to the ancient Toltecs, migrated to the western and central regions of present-day El Salvador in the 10th century. Efforts are underway to revitalize and protect these languages, despite declining speakers. Lenca, spoken by the Lenca community in rural areas of Morazán, is another indigenous language in El Salvador. Initiatives promote and teach this language.
While Spanish dominates education and media, El Salvador is influenced by other languages, particularly English due to significant emigration to the United States. English terms and expressions are adopted in technology, entertainment, and tourism. Salvadorans are becoming proficient in multiple languages, primarily English.
Thus, El Salvador’s linguistic landscape includes Spanish as the dominant language, alongside indigenous languages, foreign influences, and the adoption of anglicisms, reflecting the country’s rich culture and dynamic history.
Danish
El Salvador, con una superficie de 20 mil kilómetros cuadrados, muestra diversidad lingüística. Aunque el español es el idioma dominante, se hablan otros idiomas precolombinos en comunidades específicas. El español salvadoreño tiene características únicas, como la aspiración de la “s” final y el uso de diminutivos, incorporando expresiones locales y vocabulario regional.
Las comunidades indígenas trabajan para preservar sus lenguas ancestrales. El náhuat, hablado en áreas rurales de Ahuachapán, Sonsonate y La Libertad, fue históricamente hablado por el pueblo pipil. Los pipiles, relacionados culturalmente con los antiguos toltecas, migraron a las regiones occidental y central del El Salvador actual en el siglo X.
Se están realizando esfuerzos para revitalizar y proteger estas lenguas, a pesar de la disminución de hablantes. El lenca, hablado por la comunidad lenca en áreas rurales de Morazán, es otro idioma indígena en El Salvador. Se promueven e enseñan iniciativas para esta lengua.Aunque el español domina en la educación y los medios de comunicación, El Salvador se ve influenciado por otros idiomas, especialmente el inglés debido a la gran emigración hacia Estados Unidos. Se adoptan términos y expresiones en inglés en tecnología, entretenimiento y turismo. Los salvadoreños están adquiriendo competencia en múltiples idiomas, principalmente el inglés.
Carlos, freelance writer, analyst, and tutor
Así, el panorama lingüístico de El Salvador incluye al español como idioma dominante, junto con lenguas indígenas, influencias extranjeras y la adopción de anglicismos, lo cual refleja la rica cultura e historia dinámica del país.
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Spanish (96%)
Actual languages
Spanish (96%), Nahua (1.4%), Mayan Languages (0.7%), other (1.9%)
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in El Salvador
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 61/150 localize by translating into Spanish
- 1/150 localizes by translating into both Spanish and Salvadoran Sign Language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Qʼeqchiʼ
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Spanish, German, French, Italian, Bahasa Indonesia, Hungarian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Turkish, Russian, Japanese, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Thai and Ukrainian
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Overview
Language
Official language
Spanish (96%)
T-index
0.037%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
Other languages
Nahua (1.4%), Mayan Languages – Pipil language, Lencan languages, Cacaopera – (0.7%), other (1.9%)
English
Moderate proficiency (EF) – 50 of 111 countries/regions in the world- 9/20 position in Latin America.
Demography
Capital: San Salvador
Currency: United States dollar
Population: 6,31 m
Population density: 304/km2
Economy
GDP: 28.74 billion USD (2021)
GDP per capita: 54,551.2 USD (2021)
Exports: $6.86 billion (2021)
Statistics
Internet users: 71.7% penetration, 4.55 million
Unemployment rate: 3.8% (2022)
Urbanisation: 74% (2021)
Literacy: 90% (2020)
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numbering system, point as decimal separator and comma as separator of thousands
Date format: yyyy-mm-dd / mm-dd-yyyy
Time: 12h time system (am/pm) – except Quebec (24h)
Country code: 0020
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal
Facts and data
Economy
Imports
$14.3 billion (2021). Refined Petroleum ($1.27B), Petroleum Gas ($400M), Broadcasting Equipment ($397M), Computers ($328M), and Cars ($285M), importing mostly from United States ($3.98B), China ($2.34B), Guatemala ($1.73B), Mexico ($1.1B), and Honduras ($670M).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 29% have an account with a financial institution
• 5.7% have a credit card
• 3.5% have a mobile money account
• 5.6% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
Easy to conduct business (rated 65.3 out of 100). 8th out of 32 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, 91st worldwide out of 190 countries (2023, World Bank)
Exports
$6.86 billion (2021). Knit T-shirts ($752M), Knit Sweaters ($436M), Electrical Capacitors ($311M), Plastic Lids ($269M), and Raw Sugar ($236M), exporting mostly to United States ($2.67B), Guatemala ($1.16B), Honduras ($1.09B), Nicaragua ($492M), and Costa Rica ($280M).
Economic freedom
‘Mostly free’ (56 out of 100) 23rd amongst 32 countries in the Americas region 114th worldwide out of 186 countries (2022, Heritage Foundation and Wall Street Journal)
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 14th out of 18 Latin American and Caribbean countries, 100th out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal
Service imports (2020)
Source: OEC
Service Exports (2020)
Source: OEC
Most Specialized Products by RCA Index
Specialisation is measured using Revealed Comparative Advantage, an index that takes the ratio between El Salvador observed and expected exports in each product
Source: OEC
Most complex products by PCI
Product Complexity Index measures the knowledge intensity of a product by considering the knowledge intensity of its exporters
Source: OEC
Trade Value Relatedness vs. Most related products
Source: OEC

T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media language
Spanish
Information channels
Press freedom is guaranteed under the constitution and there is a lively media scene, says Freedom House. But journalists who report on the activities of criminal gangs, or on corruption, face harassment and acts of violence. Five national TV networks are on the air and there are scores of radio stations in the capital alone. The broadcast media are privately owned and in the hands of a small group of business interests which exercise editorial influence. There were 3.1 million internet users by 2017, around 50% of the population (via Internetworldstats). Access is unrestricted.
The press
La Prensa Grafica – daily
El Mundo – evening daily
El Diario de Hoy – daily
El Diario Co Latino – daily
El Faro – digital weekly
Television
TCS (Canal 2) – private
Canal Cuatro (Canal 4) – private
Canal Seis (Canal 6) – private
Agape TV (Canal 8) – private
Canal 12 – private
Radio
YSKL La Poderosa – commercial
FM Globo – commercial
Femenina 102.5 – commercial
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
71.7% penetration, 4.55 million
Share of web traffic by device
58.79% mobile phones, 39.70% computers (laptops and desktops), 1.44% tablet devices, others 0.08%
Median speed of mobile Internet connection
20.98 Mbps
Median speed of fixed Internet connection
31.30 Mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population: 156.5%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G): 81.6%
Most popular web search engines
Google (95.91%), Bing (3.31%), Petal Search (0.33%), Yahoo (0.25%), DuckduckGo (0.09%), Yandex (0.05%)
Most used social media
Facebook (72.17%), Instagram (11.2%), Pinterest (7.41%), Twitter (4.58%), YouTube (4.23%), Tumblr (0.18%)
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Social statistics
Life expectancy
71 years (2020)
Current healthcare expenditure
9.85% of GDP (2019)
Current education expenditure
94.1% of total expenditure in public institutions
Co2 emissions
1.12 metric tons per capita
Gender
Unfortunately, women suffer from considerable inequality. They generally they earn less, have lower positions in organizations and face strong pressures to stay at home, even though things are changing. It is still a man’s society, but women are progressively improving their status.
Sexual harassment can be a problem. Men are used to flirting with women.
Ethnicity
Due to political and social problems, inherited by colonialism, native people were forgotten and our roots almost disappeared, however, the Mayan culture is still alive in some areas along Central America. The native dialect is “nahuat”, which just a few people know. There is no predominant race.
It is common to see wealthy businesswomen/men, but some of them treat their employees without respect. This is noticeable through a different kind of communication, their expressions when talking about poor people, differences in opportunities, and mainly in salary. This situation can be clearly observed in certain contexts such as the industrial, commercial, and agricultural sectors and you can find yourself involved in implementing some decisions, in the organization, which could affect low-income employees.
Problems or impacts in the workplace are generated mainly because of gender and class position, but not by religion or ethnicity issues.
Religion
The official religion is Roman Catholic, but there are other religions such as Baptist and other denominations. You will not find any strong barriers to establishing a relationship with someone of another religion.
Class
There are different social classes, with marked differences between them. Higher classes are located in the capital and in the rest of the country it is quite rare to find rich people. 35% of the population is considered very poor and another 30% as poor.
Corruption Perception Index
El Salvador scored 33 out of 100, ranked 116 out of 180 countries worldwide.
The CPI measures the perception of corruption due to the difficulty of measuring absolute levels of corruption.
World Happiness Index
Canada ranked 49 out of 137 countries, with a score of 6.120.
The World Happiness Index measures happiness based on respondent ratings of their own lives, correlated with other life factors.
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
Tertiary education in El Salvador
Source: UNESCO
Tertiary education in El Salvador, by sex
Source: UNESCO
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Languages research
Native languages in El Salvador
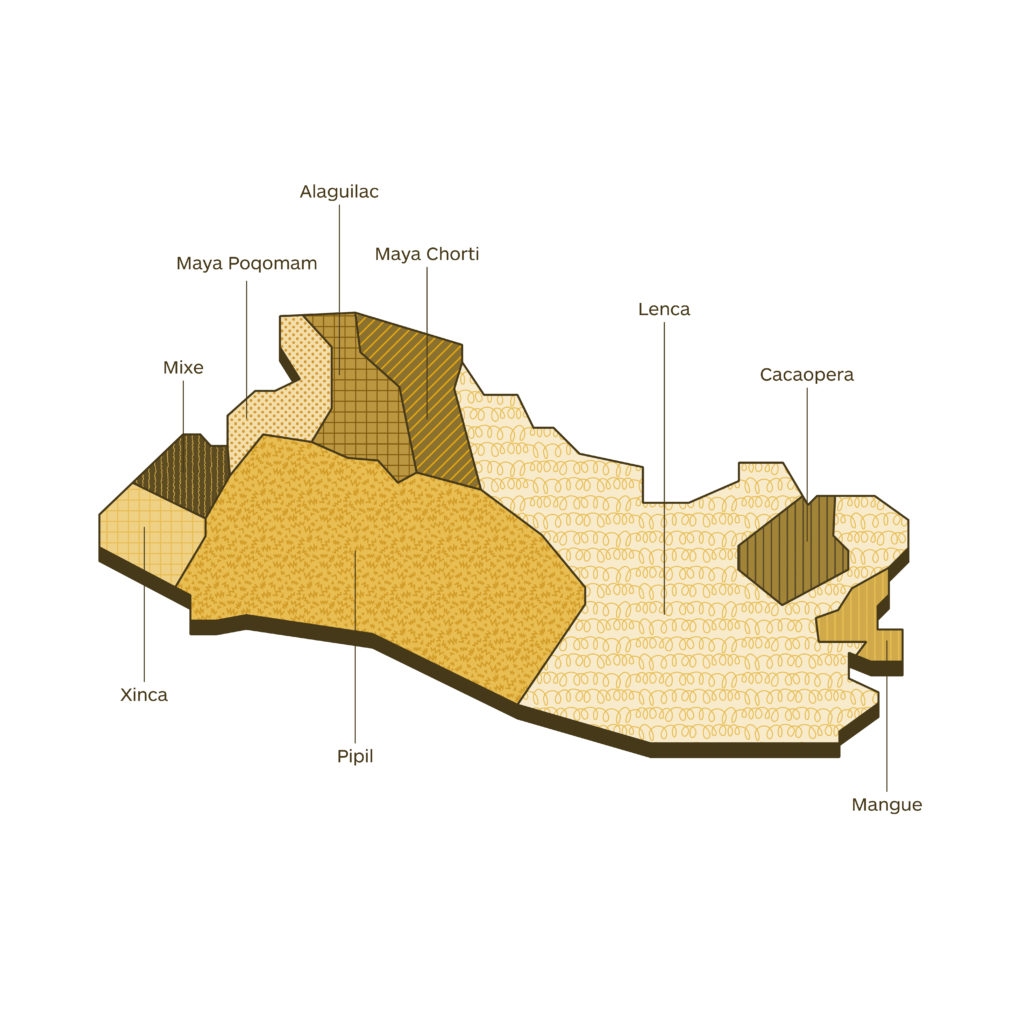
Legend
-
Lenca
-
Maya Chorti
-
Cacaopera
-
Mangue
-
Alaguilac
-
Maya Poqomam
-
Pipil
-
Mixe
-
Xinca
The geographical distribution of languages that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: ohne Titel, IStock


