Europe
To which language should you translate to localize in Poland?
What we know from our community
“Poland speaks one official language – Polish which belongs to the group of Slavic languages.
The population is homogenous or has been so far as the situation is pretty dynamic with
over two million Ukrainian war refugees residing in Poland these days. Ukrainian has
become the second language in public interest institutions such as banks or public transport
or official news websites such as onet.pl . It may soon be worth considering targeting that
growing minority with translations to Ukrainian language.
There are some other ethnical minorities living in Poland such as German minority living in
the south-west region of Silesia or Belarussian minority in the north-eastern part of Poland
as well as Kashubian minority in the Pomeranian district of Poland. Yet their presence and
diversity are only reflected in double geographical names in the regions.
When it comes to homogeneity of Polish language, its official version taught at school and
present In media does not recognize dialects occurring in some regions such as Poznan or
Cracow which are mostly used in spoken language and treated as a tourist attraction.”
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Polish (96.6%; 35.44 mln)
Actual languages
Polish (96.6%; 35.44 mln), German (1.3%; 476k), Ukrainian (0.6%; 220k), Belarusian (0.5%; 183k), other (1.0%; 366k)
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in Poland
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 109/150 localize by translating into Polish
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish and German
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish and Russian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish and German
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish and Ukrainian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish and Polish Sign Language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish, French, Spanish, German and Russian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish, French and Simplified Chinese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish, French, Spanish, German, Italian, Portuguese, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Japanese, Arabic, Czech, Hungarian, Nederland and Swedish
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish, French, Spanish, German, Italian, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Japanese, Hungarian, Thai, Ukrainian, Turkish, Romanian and Bahasa Indonesia
- 1/150 localizes by translating into French, Spanish, German, Italian, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Japanese and Korean
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Polish, French, Spanish, German, Italian and Simplified Chinese
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Overview
Language
Official language
Polish (96.6%)
T-index
0.69%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
Other languages
German (1.3%), Ukrainian (0.6%), Belarusian (0.5%), other (1.0%)
English
High proficiency (EF) – 15 of 116 countries/regions in the world- 13/35 position in Europe.
Demography
Capital: Warsaw
Currency: Polish złoty
Population: 36.69 mln
Population density: 120/km2
Economy
GDP: 809.2 billion USD (2023)
GDP per capita: 22,056.7 USD (2023)
Exports: $346 billion (2022)
Statistics
Internet users: 88.1% penetration, 35.75 million
Unemployment rate: 4.9% (2024)
Urbanisation: 60.2% (2023)
Literacy: 100% (2021)
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numerals and comma as decimal separator
Date format: yyyy-mm-dd / dd-mm-yyyy
Time: 24h time system
Country code: 0048
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal/Worlddata.info
Facts and Data
Economy
Imports
$382 billion (2022). Crude Petroleum ($16.5B), Cars ($13.5B), Motor vehicles; parts and accessories (8701 to 8705) ($10.2B), Refined Petroleum ($8.86B), and Broadcasting Equipment ($6.85B), importing mostly from Germany ($88.9B), China ($43.9B), Italy ($20B), Netherlands ($18.6B), and Czechia ($16.2B).
In 2022, Poland was the world’s biggest importer of Oxometallic or Peroxometallic Acid Salts ($3.06B), Carbon ($714M), Roofing Tiles ($97.6M), and Lead Oxides ($17.6M).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 95.7% have an account with a financial institution
• 24.4% have a credit card
• 58.4% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
It is very easy to conduct business (rated 76.4 out of 100) ranked 25th out of 34 OECD high income countries, ranked 40th out of 190 countries worldwide (2023, World Bank).
Exports
$346 billion (2022). Motor vehicles; parts and accessories (8701 to 8705) ($15.3B), Electric Batteries ($9.55B), Computers ($6.73B), Seats ($6.67B), and Other Furniture ($6.66B), exporting mostly to Germany ($93.1B), Czechia ($22.4B), France ($19.8B), United Kingdom ($17.2B), and Netherlands ($16.3B).
In 2022, Poland was the world’s biggest exporter of Wood Crates ($1.24B), Razor Blades ($891M), Frozen Fruits and Nuts ($719M), Newspapers ($409M), and Insulating Glass ($374M).
Main local online stores
Allegro.pl, Ceneo, RTV EURO AGD, Skapiec.pl, Komputronik, eBay, Zalando, empik.com.
Economic freedom
‘Moderately free’ (66 out of 100) ranked 23rd out of 44 European countries, ranked 42nd out of 184 countries worldwide (2024, Heritage Foundation and Wall Street Journal).
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 26th out of 39 European countries, 41st out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal
Service Imports (2020)
Service Exports (2020)
Source: OEC
Trade balance of goods from 2012 to 2022
Source: Statista
Historical Data Trade Imports
The following section uses historical trade data imports from partners of Poland.
Historical Data Trade Exports
The following section uses historical trade data exports from partners of Poland.
Source: OEC
The Top Export Opportunities for Poland by Relatedness
Relatedness measures the distance between a country's current exports and each product by showing only products that Poland is not specialized in.
Poland's Most Complex Exports
The Product Complexity Index (PCI) measures the knowledge intensity of a product by considering the knowledge intensity of its exporters.
Source: OEC
Poland's Most Specialized Products
Specialization is measured using Revealed Comparative Advantage (RCA), an index that takes the ratio between Poland observed and expected exports in each product.
Source: OEC
Perception of products made in selected countries in 2017
Source: Statista
Which attributes do you associate with products made in Poland?
Source: Statista
Market Growth Imports (2020)
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start importing that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Market Growth Exports (2020)
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start exporting that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Source: OEC
Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP)
Source: WorldBank
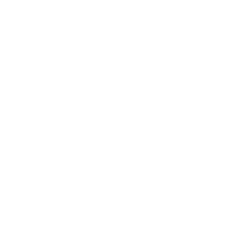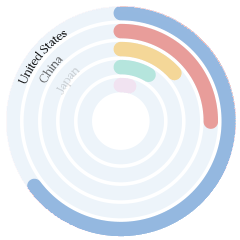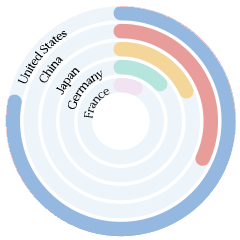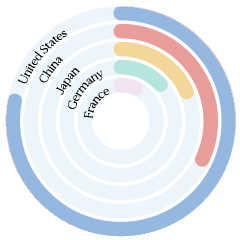
T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media language
Polish
Information channels
Poland’s broadcasting market is the largest in Eastern and Central Europe. TV is the leading medium and three players – state-owned TVP and privately-owned TVN and Polsat – dominate the market. Many non-state media outlets are owned by foreign concerns, particularly German companies. Agora – the publisher of Gazeta Wyborcza newspaper – is the main domestic media group. There are hundreds of newspaper titles, most of them local or regional. The top-selling tabloid, Fakt, is owned by Germany-based publisher Axel Springer. The constitution guarantees freedom of expression and forbids censorship. But critics cried foul when the newly-elected conservative Law and Justice government introduced a bill in late 2015 to allow ministers to appoint the heads of TVP and public Polish Radio. The move prompted the European Commission to look into any potential threat to freedom of expression. The public media “have been transformed into government propaganda mouthpieces”, Reporters Without Borders said in 2018. Freedom House says private media that criticise the government have experienced pressure from regulators and a fall in advertising revenue from state-run companies. Some ruling party members have called for changes in the law to reduce foreign ownership of the media, advocating a “repolarisation” of the sector.
The press
Gazeta Wyborcza – mass-circulation daily
Rzeczpospolita – influential daily
Fakt – mass-circulation tabloid daily
Super Express – mass-circulation tabloid daily
Dziennik Gazeta Prawna – economic daily
Polityka – weekly
Wprost – weekly
Newsweek Polska – weekly
The Warsaw Voice – English-language weekly
Warsaw Business Journal – English-language weekly
Television
Telewizja Polska (TVP) – public, operates national, regional and thematic networks
TVN – commercial, also operates news channel TVN 24
Polsat – commercial channel and pay-TV operator
Canal+ – pay-TV operator
Radio
Polish Radio – public, operates five national networks and many regional stations
TheNews.pl – Polish Radio’s news site, in English
RMF FM – commercial
Radio Zet – commercial
Radio Maryja – controversial Catholic station, run by Redemptorist Order
News agency
Polish News Agency (PAP) – state-run
Wirtualna Polska – portal
Onet.pl – portal
Interia – portal
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
88.1% penetration, 35.75 million
Share of web traffic by device
69.97% mobile phones, 29.39% computers (laptops and desktops), 0.62% tablet devices, others 0.02%
Median speed of mobile Internet connection
42.12 mbps
Median speed of fixed Internet connection
139.28 mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population: 130.8%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G): 96.3%
Most popular web search engines
Google (95.6%), Bing (2.83%), DuckDuckGo (0.68%), Yahoo! (0.44%), Yandex Ru (0.32%), other (0.12%).
Most used social media
Facebook (87.55%), Instagram (4.28%), Pinterest (2.83%), Twitter (2.55%), YouTube (1.93%), Tumblr (0.35%), reddit (0.32%), Other (0.2%).
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Social statistics
Life expectancy
77 yrs (2022)
CO2 emissions
7.4 metric tons per capita
Corruption perceptions Index
Poland scored 55 out of 100, ranked 45 out 180 countries worldwide.
Current health expenditure
6.68% of GDP (2022)
Current education expenditure
93.5% of total expenditure in public institutions
World Happiness Index
Poland ranked 48 out of 137 countries, with a score of 6.123.
Glass Ceiling Index
68.2 out 100, ranked 10th out of 29 countries.
The glass-ceiling index measures the environment for working women combining data on higher education, labor-force participation, pay, child-care costs, maternity and paternity rights, business-school applications, and representation in senior jobs.
Religion
Poland is predominantly a catholic country and this is outwardly manifested. Churchgoing is prevalent. Also various religious holidays and traditions are observed. It is common to profess adherence to church rules and dogma for the sake of appearance but, in practice, true observance is not so widespread. In public, people tend to be very uncritical about the church and although in a closer group of friends they may be more critical, they will still follow most of the traditions associated with the church.
Ethnicity
After WW II, Poland became ethnically very homogenous. This had two effects: lack of conditions in which ethnic tensions arose and, at the same time, lack of knowledge and therefore understanding and appreciation of ethnic differences. As a result, ethnic differences may be noticed more in Poland than in more diverse countries. On Polish streets, there are few people who do not look Polish. There are few Asians and even fewer black people and most live in the largest cities.
Graduates (tertiary education)
More adults in Poland are obtaining a tertiary degree today than a decade ago. While 32% of young adults had attained a tertiary education in 2008, 44% of them had in 2018, a similar attainment rate as the OECD average (2019)
Gender
The approach to gender is peculiar in Poland. On one hand, women have been working outside the home in huge numbers at least since the end of the Second World War. Even as early as the 19th century, they played important social roles and participated in decision-making on the family and community level, about economic matters. In today’s Poland, statistically, they are better educated than Polish men but they earn less money (the gender wage gap is about 30%) and they are discriminated at work place on basis of age, marital and parental status and appearance, despite is being illegal. At the same time, women are supposed to be (and in most cases are) treated with respect and there is a certain double standard of morality where women are expected to behave with greater moral sobriety than men.
Class
Although Poland was communist for a very long time, it remains a very class-based society, even if it is not just a simple division according to the wealth of the individual. People tend to socialise very much with their own kind. Education is very important and it is unlikely that people with high education will socialize with those who are not educated. It is still quite uncommon for an educated man to marry a non- educated woman.
Class is also decided by family status. People from the rural areas are generally perceived as lower class. In Warsaw, people are probably judged more on the basis of their own achievements and money. It may be important to note that Poland had a large aristocratic population before WW II, however, most aristocrats were killed during the war and during the Stalinist area, with the few survivors emigrating or marrying ordinary Poles.
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
Country Curiosities
Poland’s name comes from the Slavic word “Polska,” which is derived from “pole,” meaning “field” or “plain.” It reflects the flat, fertile landscape where early Slavic tribes settled. Shaped by the erosion of Europe’s oldest mountains, the land was ideal for agriculture. “Polska” essentially means “land of the plains,” connecting Poland’s name to its agricultural roots and the deep bond between its people and the land.
Additionally…
- Poland is home to many influential figures, including Copernicus, Curie, Chopin, and John Paul II, in fact it has won 18 Nobel Prizes in total.
- Poland’s Constitution, adopted in 1791, was the 2nd in the world.
- Poland didn’t exist on maps for 123 years and was occupied or fought for freedom 43 times since 1600.
- Polish is one of the world’s most difficult languages to learn.
- Polish last names change depending on gender, e.g., Kowalski vs. Kowalska.
- Poland is first in the EU for exports of monitors and beamers.
- Poland is among the largest producers of apples, mushrooms, and amber globally.
- Over 71% of Polish citizens identify as Roman Catholic.
- Poland is one of the fastest-growing countries in the EU.
- Poland remains one of the most peaceful countries, according to UNICEF.
- Poland is the 8th largest country in Europe with a population of over 38 million.
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Languages Research
Languages spoken in Poland
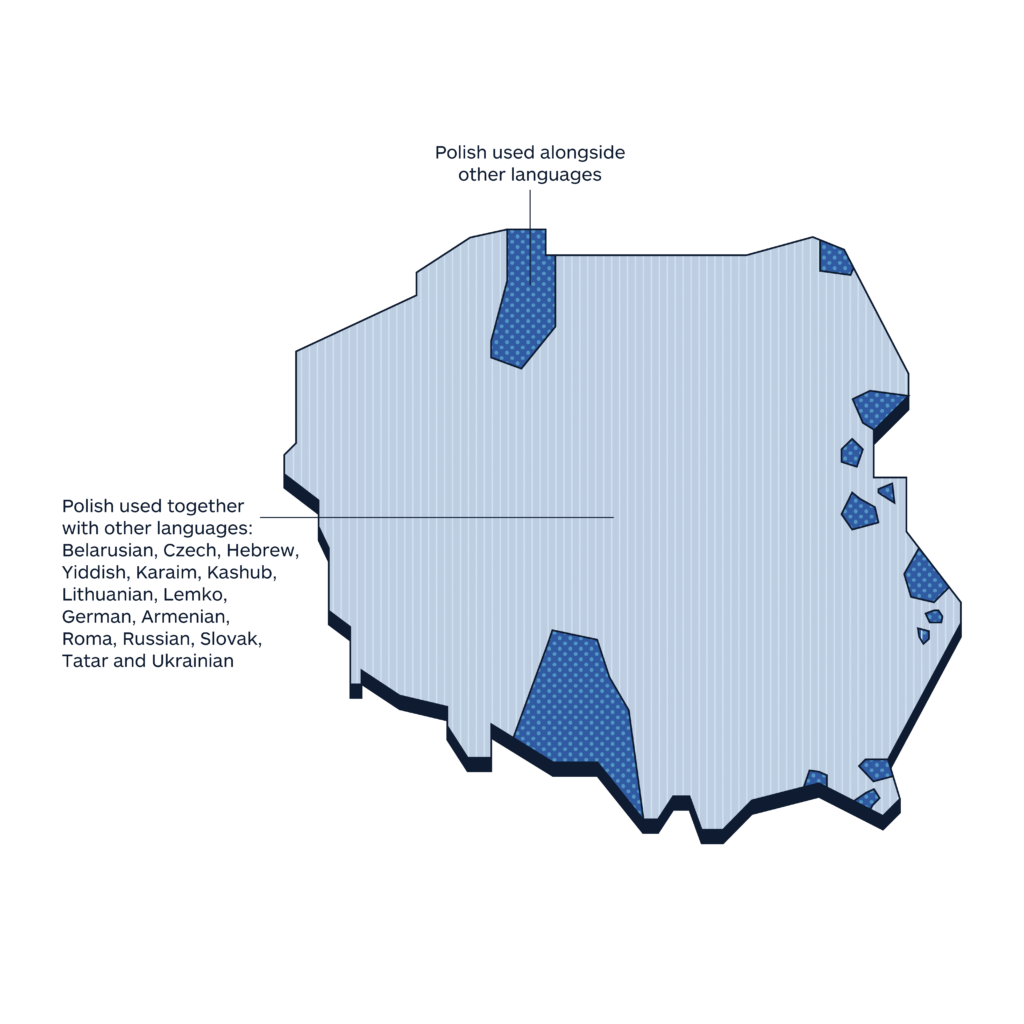
Legend
-
Polish used together with other languages
-
Polish used alongside other languages
The geographical distribution of languages that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: Pawel Czerwinski, Unsplash


