Asia
To which language should you translate to localize in Singapore?
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Chinese (52%; 3.07 mln), English (29.8%; 1.76 mln), Malay (11.9%; 704k) and Tamil (4.4%; 260k)
Actual languages
Chinese (52%; 3.07 mln), English (29.8%; 1.76 mln), Malay (11.9%; 704k), Tamil (4.4%; 260k), Hindi (1.2%; 71k), other (0.7%; 41k)
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in Singapore
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 103/150 localize by translating into English
- 9/150 localize by translating into both English and Simplified Chinese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese, Bahasa Indonesia, Burmese, Hindi, Tamil, Bengali and Thai
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Korean, French, Japanese, Italian and Russian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Korean, French and Japanese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Korean, French and Japanese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese and French
- 1/150 localizes by translating into English, Simplified Chinese and Singapore Sign Language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Simplified Chinese
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Overview
Language
Official language
Chinese (52%), English (29.8%), Malay (11.9%) and Tamil (4.4%).
Actual languages
Chinese (52%), English (29.8%), Malay (11.9%), Tamil (4.4%), Hindi (1.2%), other (0.7%).
Most studied languages
Mandarin (for non-Chinese), Malay (for non-Malays), Indonesian (for non-Malays), Arabic, Japanese (only for Chinese), French and German
T-index
0.27%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
English
Very high proficiency (EF) – 2 of 113 countries/regions in the world- 1/23 position in Asia.
Demography
Capital: Singapore
Currency: Singapore dollar
Population: 5.91 milion
Population density: 7/km2
Economy
GDP: 501.43 billion USD (2023)
GDP per capita: 84,734.3 USD (2023)
Exports: $379 billion (2022)
Statistics
Unemployment rate: 3.6% (2022)
Urbanisation: 100% (2023)
Literacy: 98% (2021)
Internet users: 96% penetration, 5.79 million
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numbering system, point as decimal separator and comma as separator of thousands.
Date format: yyyy-mm-dd / dd-mm-yyyy
Time: 24h time system
Country code: 0065
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal/Worlddata
Facts and data
Economy
Imports
$424 billion (2022). Integrated Circuits ($76B), Refined Petroleum ($58.5B), Crude Petroleum ($32.6B), Gold ($17.5B), and Machinery Having Individual Functions ($11.6B), importing mostly from China ($73.3B), Malaysia ($53.8B), United States ($41.4B), Chinese Taipei ($38.6B), and South Korea ($22.5B).
In 2022, Singapore was the world’s biggest importer of Other Glass Articles ($480M) and Other Nickel Products ($377M).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 97.2% have an account with a financial institution
• 41.7% have a credit card
• 30.6% have a mobile money account
• 56.6% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
Very Easy to conduct business (86.2 out of 100) 1st out of 25 East Asia-Pacific countries, 2nd worldwide out of 190 countries (2023, World Bank).
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 1st out of 17 South East Asia, East Asia and Oceania countries, 5th out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Exports
$379 billion (2022). Integrated Circuits ($81.9B), Refined Petroleum ($62.9B), Machinery Having Individual Functions ($15.4B), Gold ($13.1B), and Gas Turbines ($8.48B), exporting mostly to Hong Kong ($51.6B), China ($51.2B), Malaysia ($35.9B), United States ($28.9B), and Indonesia ($22.5B).
In 2022, Singapore was the world’s biggest exporter of Glass Working Machines ($1.21B), Incomplete Movement Sets ($72.3M), and Human Hair ($15M).
Main local online stores
Shopee, Lazada, Amazon, Qoo10, EZuBy, eBay, Zalora, Courts Singapore, Castlery, Love, Bonito
Economic freedom
‘Free’ (83.5 out of 100) 1st out of 45 countries in Asia Pacific and 1st worldwide out of 184 countries (2024, Heritage Foundation and Wall Street Journal).
Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal

Tiny Giant, Major Harmony
What's Imminent In Singapore
Each month, we spotlight a country with its own unique characteristics. Using analytical lens, we explore What’s Imminent in the linguistic, cultural, and economic tapestry to unveil its true character. Join us in this insightful exploration to understand the distinctive dynamics of each region.
Read it now!Service Imports (2020)
Service Exports (2020)
Source: OEC
Trade balance of goods from 2013 to 2023
Source: Statista
Historical Data Trade Imports
The following section uses historical trade data imports from partners of Singapore.
Historical Data Trade Exports
The following section uses historical trade data exports from partners of Singapore.
Source: OEC
Singapore's Most Specialized Products
Specialization is measured using Revealed Comparative Advantage (RCA), an index that takes the ratio between Singapore observed and expected exports in each product.
Source: OEC
Singapore's Most Complex Exports
The Product Complexity Index (PCI) measures the knowledge intensity of a product by considering the knowledge intensity of its exporters.
The Top Export Opportunities for Singapore by Relatedness
Relatedness measures the distance between a country's current exports and each product by showing only products that Singapore is not specialized in.
Source: OEC
Perception of products made in selected countries in 2017
Source: Statista
Which attributes do you associate with products made in Singapore?
Source: Statista
Market Growth Imports
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start importing that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Market Growth Exports
This score represents the likelihood that the given country will start exporting that product in the next few years. It forecasts the opening of a new specific market.
Source: OEC
Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP)
Source: WorldBank
Top 10 e-commerce sites in Singapore as of third quarter of 2019, by monthly traffic (in million clicks)
Distribution of e-commerce payment methods in Singapore in 2019
Sources: SimilarWeb; iPrice Group
Source: WorldPay
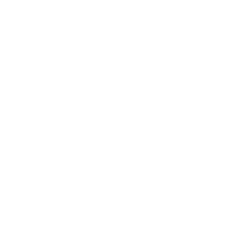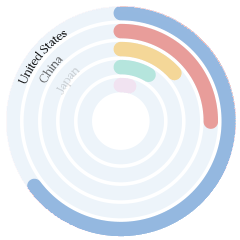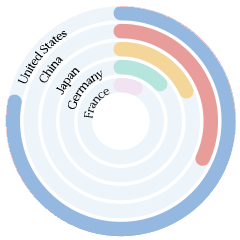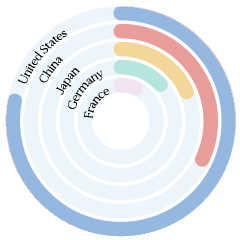
T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media main languages Mandarin, Malay and Indian, English
Information channels
Singapore’s media are highly developed and tightly controlled. There are two major players. Singapore Press Holdings is linked to the ruling party and has a near-monopoly of the press. MediaCorp, owned by a state investment agency, runs TV and radio stations. Both companies have extended their dominance to include online media, says Reuters Institute. Media have incurred harsh criminal penalties for “speech deemed to be seditious, defamatory, or injurious to religious sensitivities”, says Freedom House. Newspapers occasionally publish critical content, although news coverage is generally pro-government. Reporters Without Borders says the range of issues and public figures that are off limits for media coverage is growing and that self-censorship is widespread.
The press
Singapore Press Holdings (SPH) – publishes multiple newspapers, magazines, websites
The Straits Times – published by SPH
Business Times – published by SPH
Today – published by Mediacorp
Television
MediaCorp – operates entertainment-based Channel 5 and Channel 8, Malay channel Suria, Mandarin-language Channel U
Channel NewsAsia – news TV operated by MediaCorp
Radio
MediaCorp – operates more than a dozen stations including English-language news and talk station 938Live, music stations and Chinese, Malay and Indian services
SPH – operates English-language One FM and Kiss 92, Mandarin station UFM
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
96% penetration, 5.79 million
Share of web traffic by device
59.28% mobile phones, 37.94% computers (laptops and desktops), 2.77% tablet devices.
Median speed of mobile Internet connection
95.18 Mbps
Median speed of fixed Internet connection
263.51 Mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population
162.2%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G): 99.3%
Most popular web search engines
Google (94.33%), Bing (3.16%), Yahoo! (1.37%), DuckDuckGo (0.39%), Yandex (0.3%), other (0.45%).
Most used social media
Facebook (44.31%), Twitter (16.44%), Instagram (11.82%), Pinterest (8.17%), YouTube (7.56%), LinkedIn (7.07%), reddit (3.65%), other (0.98%).
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Social statistics
Life expectancy
83 yrs (2022)
Corruption perceptions Index
Singapore scored 83 out of 100, ranked 5th out of 180 countries worldwide.
Current health expenditure
5.57% of GDP
CO2 emissions
7.7 metric tons per capita
Current education expenditure
91.8% of total expenditure in public institutions
World Happiness Index
Singapore ranked 27th out of 146 countries, with a score of 6.480.
Cultural Curiosities
Singapore is home to three main ethnicities: Chinese, Malay and Indian. As in other Asian countries, the concept of “face” – relating to a person’s reputation, influence, dignity and honour – is central to Singaporean culture. “Have you eaten?” is a very common greeting in Singapore: don’t be confused, it’s the equivalent of “How’s it going?”.
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
Resident population in Singapore as of June 2019, by ethnic group (population in thousands)
Multi-language literacy had become more prevalent
Department of Statics Singapore
Highest qualification attained
(of residents aged 25 years and over)
Chinese: Literate resident population aged 15 and over by ethnic group and language literate in
Department of Statics Singapore
Malays: Literate resident population aged 15 and over by ethnic group and language literate in
Indians: Literate resident population aged 15 and over by ethnic group and language literate in
Department of Statics Singapore
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Country Curiosities
Singapore is a relatively new country, officially becoming independent on August 9, 1965, after separating from Malaysia. This modern metropolis has transformed remarkably from a low-income nation to a high-income state, boasting one of the world’s largest GDP growth rates. After British colonial rule ended in 1963, Singapore joined the Federation of Malaysia. However, due to political and economic differences, the union dissolved two years later. Malaysia chose to break ties, leaving Singapore to continue as an independent state. Despite these challenges, Singapore has made significant strides in development and prosperity.
Additionally…
- Since 1905, Singapore has changed its time zones six times. It currently follows GMT+8 to align with Malaysia, though it technically should be GMT+7.5.
- Singapore, one of the world’s 20 smallest countries, has a main island 42 km long and 23 km wide, totaling just 683 square kilometers.
- The Tanjong Pagar Centre, opened in 2016, is Singapore’s tallest building at 290 meters, exceeding the usual 280-meter height limit by special permission.
- Sang Nila Utama, a Palembang prince, named the island Singapura, meaning ‘lion city’ in Sanskrit, after mistakenly thinking he saw a lion there.
- According to the World Bank, Singapore is the second easiest place to do business after New Zealand.
- Singapore is one of only three modern city-states, alongside Monaco and the Vatican.
- Singapore is the world’s fifth largest arms importer (Stockholm International Peace Research Institute).
- With over 3000 kilometers of roads, Singapore’s road network could stretch the distance between Singapore and Hong Kong.
- Singapore’s passport is the world’s most powerful, offering visa-free access to 193 countries (Henley Passport Index).
- Singapore is the world’s most expensive city, driven by its booming business environment.
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Languages research
English as a first language – but it is significant how important the second language is to safeguard asian cultural identities.
Singapore has a bilingual education policy, where all students in government schools are taught English as their first language. Students in Primary and Secondary schools also learn a second language called their “Mother Tongue” by the Ministry of Education, where they are either taught Mandarin, Malay, or Tamil. English is the main language of instruction for most subjects, while Mother Tongue is used in Mother Tongue lessons and moral education classes. This is because Singapore’s “bilingualism” policy of teaching and learning English and Mother Tongue in primary and secondary schools is viewed as a “cultural ballast” to safeguard Asian cultural identities and values against Western influence.
Chinese: Proportion of resident population aged 15 and over who spoke English most frequently at home, by ethnic group and highest qualification attained
Malays: Proportion of resident population aged 15 and over who spoke English most frequently at home, by ethnic group and highest qualification attained
Department of Statics Singapore
Indians: Proportion of resident population aged 15 and over who spoke English most frequently at home, by ethnic group and highest qualification attained
Chinese: Resident population aged five years and over by ethnic group and language most frequently spoken at home
Department of Statics Singapore
Malays: Resident population aged five years and over by ethnic group and language most frequently spoken at home
Indians: Resident population aged five years and over by ethnic group and language most frequently spoken at home
Department of Statics Singapore
Non residents in Singapore
In 2019, work-permit holders and foreign domestic workers comprised 56% (or about 941,000) of the 1.68 million non-residents in Singapore. Singapore continues to have a strong demand for low-wage migrant workers, and their numbers will likely remain substantial in the years to come. It is necessary to work resolutely towards enhancing the working and living conditions of migrant workers who suffer deplorable hygiene conditions and overcrowding in the foreign workers’ dormitories. The foreign workers live in Singapore’s dormitories, where 10 to 20 men are often packed into a single room. These utilitarian complexes on the city-state’s periphery have become hives of infection, revealing a blind spot in Singapore’s previously vaunted coronavirus response. As of April 28, these dorms were home to 85% of Singapore’s 14,951 cases.
The term Foreign worker refers to semi-skilled or unskilled immigrants who work primarily in the manufacturing, construction, and domestic services sectors. Most of them come from places such as the People’s Republic of China, Indonesia, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, the Philippines and Thailand, under bilateral agreements between Singapore and these countries.
Foreign Talents refers to foreigners with professional qualifications or acceptable degrees who work at the highest end of Singapore’s economy. They mostly come from India, Australia, the Philippines, the People’s Republic of China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Europe, New Zealand and the United States.
Non Residents composition in Singapore
The stability of society is rooted in the confucian mentality and it hinders the improvement of social conditions and the achievement of
Power distance and Individualism Index, Singapore
POWER DISTANCE
Chinese and Indian Singaporeans are generally regarded as business-savvy ethnic groups as they tend to be profit-oriented, dominating the political and economic facets of society. The Malay population is often considered to be less economically competitive and more content with making ends meet.
The power distance dimension addresses the fact that all individuals in societies are not equal – it expresses the attitude of the culture towards these social inequalities. Power Distance is defined as the extent to which the less powerful members of institutions and organisations within a country expect and accept that power is distributed unequally.
Singapore scores high on this dimension (rating of 74). With a Confucian background (the Chinese), they normally have a syncretic approach to religion, which is also the dominant approach in Singapore. One of the key principles of Confucian teaching is the stability of society, which is based on unequal relationships between people. Confucius distinguished five basic relationships: ruler-subject; father-son; older brother-younger brother; husband-wife; and senior friend-junior friend. These relationships are based on mutual and complementary obligations. Here we can see the high PDI as a consequence.
Power is centralised and managers rely on their bosses and on rules. Employees expect to be told what to do. Control is expected and attitude towards managers is formal. Communication is indirect and the information flow is selective. We can see the high PDI also in the first of the government’s defined five “shared values”: Nation before community and society above self.
INDIVIDUALISM
Singapore, with a score of 20 is a collectivistic society. This means that the “We factor” is important, people belong to in-groups (families, clans or organisations) who look after each other in exchange for loyalty. Here we can also see the second key principle of the Confucian teaching: The family is the prototype of all social organisations. A person is not primarily an individual; rather, he or she is a member of a family.
The geographical distribution of languages that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: Victor, Unsplash


