Europe
To which language should you translate to localize in Slovenia?
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Slovenian (91.1%)
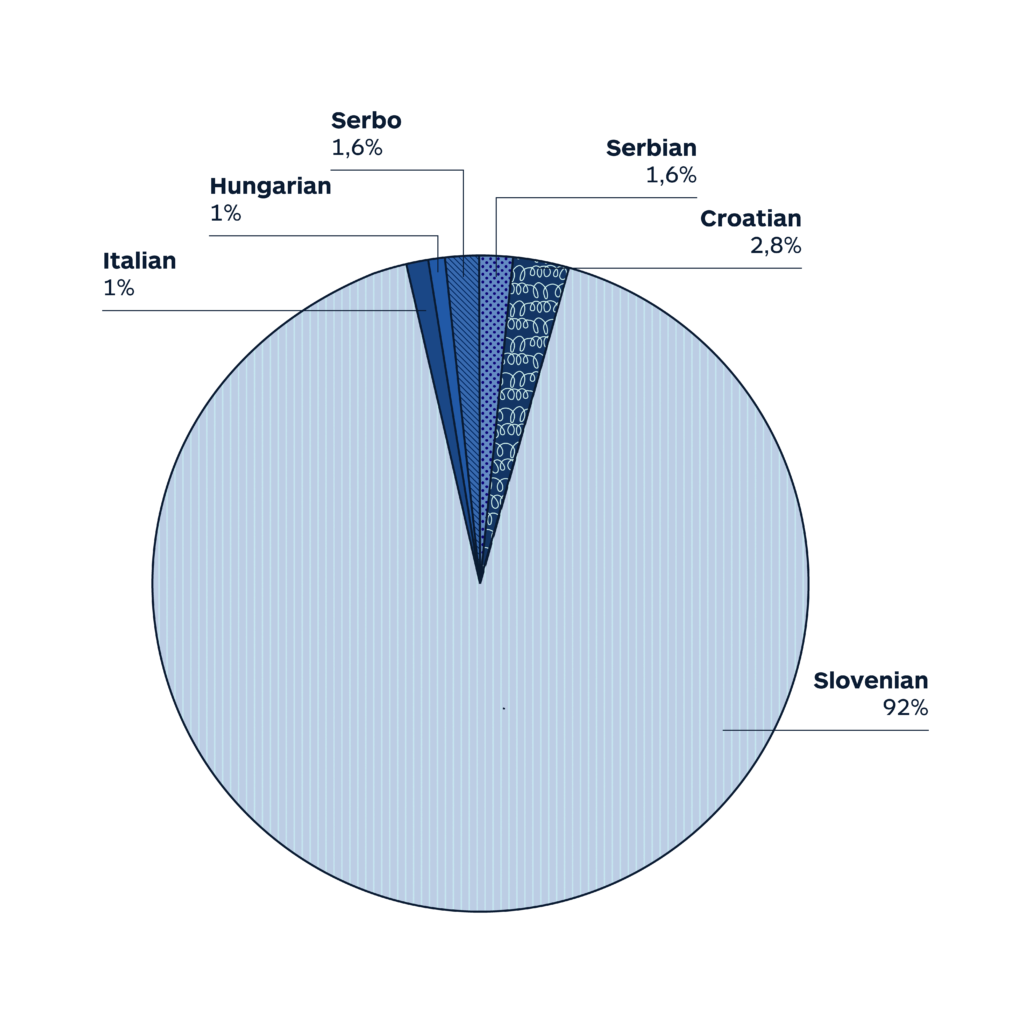
Actual languages
Slovenian (91.1%), Croatian (3.2%), Serbian (1.3%), Italian (1.1%), Hungarian (0.9%), other (2.4%).
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in Slovenia
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 66/150 localize by translating into Slovenian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Slovenian, French and Simplified Chinese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Slovenian and Slovenian Sign Language
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Italian
- 1/150 localizes by translating into both French and German
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Italian, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Korean and Japanese
- 1/150 localizes by translating into Italian, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Japanese, Bahasa Indonesia, Hungarian, Polish, Turkish, Romanian, Thai and Ukrainian
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Introduction
Language
Official language
Slovenian (91.1%)
T-index
0.058%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
Other languages
Croatian (3.2%), Serbian (1.3%), Italian (1.1%), Hungarian (0.9%), other (2.4%).
Demography
Capital: Ljubljana
Currency: Euro
Population: 2,10 m
Population density: 104/km2
Economy
GDP: 61.75 USD (2021)
GDP per capita: 29,291.4 USD (2021)
Exports: $37.5 billion (2020)
Statistics
Internet users: 90% penetration, 1.87 million
Unemployment rate: 4.7% (2021)
Urbanisation: 55.44% (2021)
Literacy: 99% (2019)
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numerals and comma as decimal separator, space as thousands separator
Date format: dd-mm-yyyy
Time: 24h time system
Country code: 00386
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal
Facts and data
Economy
Imports
$40.7 billion (2020). Packaged Medicaments ($5.57B), Cars ($2B), Refined Petroleum ($1.36B), Motor vehicles; parts and accessories (8701 to 8705) ($1.02B), and Delivery Trucks ($751M), importing mostly from Germany ($5.4B), Switzerland ($4.87B), Italy ($3.9B), China ($3.36B), and Austria ($3.19B).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 98% have an account with a financial institution
• 44% have a credit card
• 55% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
It is very easy to conduct business (rated 76.5 out of 100) ranked 23rd out of 34 OECD high-income countries, and 37th out of 190 countries worldwide (2022, World Bank).
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 21st out of 39 European countries, 33rd out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Exports
$37.5 billion (2020). Packaged Medicaments ($6.11B), Cars ($3.37B), Motor vehicles; parts and accessories ($978M), Refined Petroleum ($681M), and Vaccines, blood, antisera, toxins and cultures ($596M), exporting mostly to Germany ($6.71B), Italy ($3.53B), Switzerland ($3.47B), Croatia ($2.98B), and Austria ($2.44B).
Main local online stores
Amazon, eBay and Zalando. Other top retail sites include Ceneje.si, Mimovrste.si, Nakupovanje.net, EnaA.com, Mercator.si and Trgovine.net.
Economic freedom
‘Moderately free’ (rated 68.5 out of 100) ranked 22nd out of 44 European countries and 37th out of 186 countries worldwide (2022, Heritage Foundation and Wall Street Journal).
Service Imports (2017)
Source: OEC
Service Exports (2017)
Source: OEC
Most complex products by PCI Index
Product Complexity Index measures the knowledge intensity of a product by considering the knowledge intensity of its exporters
Source: OEC
Most specialised products by RCA Index
Specialisation is measured using Revealed Comparative Advantage, an index that takes the ratio between Slovenia observed and expected exports in each product
Source: OEC
Export Opportunities by Relatedness
Relatedness measures the distance between a country's current exports and each product, the barchart show only products that Slovenia is not specialized in
Source: OEC
Share of payment methods offered by corporations in 2019 in Slovenia, by method
Source: EOS Groppe

T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media language
Slovenian, English
Information channels
Public RTV Slovenia and private networks Pop TV and Kanal A are the main players in the TV sector. Most households subscribe to cable, IPTV or satellite packages. There are scores of commercial and public radio stations. The main newspapers are privately-owned. The constitution supports freedom of expression, but journalists can be compelled by law to reveal their sources and defamation is a criminal offence, says Freedom House.
The press
Dnevnik – Ljubljana-based daily
Delo – Ljubljana-based daily
Vecer – Maribor-based daily
Slovenske Novice – daily tabloid
Finance – business daily
Nedeljski dnevnik – weekly
Mladina – weekly
Primorske Novice – regional daily
The Slovenia Times – English-language weekly
Television
RTV Slovenia – public, operates national and regional services
Pop TV – commercial
Kanal A – commercial
TV3 – commercial
Radio
RTV Slovenia – public, operates national and regional services
Radio Hit – commercial
Radio City – commercial
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
90% penetration, 1.87 million
Share of web traffic by device
38.78% mobile phones, 59.61% computers (laptops and desktops), 1.59% tablet devices, others 0.02%
Median speed of mobile Internet connection
46.04 Mbps
Median speed of fixed Internet connection
61.26 Mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population: 111.7%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G): 86.0%
Most popular web search engines
Google (95.95%), Bing (3.16%), Duckduckgo (0.33%), Najdi.si (0.24%), Yahoo (0.13%), Yandex (0.09%)
Most used social media
Facebook (75.06%), Twitter (10.01%), Pinterest (6.19%), Instagram (5.56%), YouTube (1.95%), Reddit (0.52%)
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Social statistics
Life expectancy
81 yrs (2020)
Average age of the population
44.5 yrs (2020)
Health expenditure
8.52% of GDP
Ethnicity
Ethnic Slovenes represent around 98% of the population. Ethnicity does not have an impact on the workplace as long as foreigners, immigrants or minorities are fluent in the Slovene language. The number of expats living in Slovenia is increasing every year. They usually come for work purposes and hold senior positions in the workplace.
Religion
Most Slovenes are Roman Catholic.
Gender
Women and men are regarded as equals in Slovenia. Men are still considered the main providers in the family and women have a major role in caring for children and the home. In the workplace, women still face many challenges. There are few women in top leadership positions in the public and private sector. Women may be paid less for the same work as their male counterparts.
Graduates (tertiary education)
In Slovenia, tertiary attainment among 25-34 year-olds increased by 11 percentage points between 2008 and 2018 (from 30% to 41%), but is still below the OECD average of 44%. Despite this smaller share, those adults who do complete tertiary education in Slovenia tend to go for longer studies: 42% of those with a tertiary degree hold a master’s or equivalent, compared with 33% on average across OECD countries (2019)
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
The language research that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: Balkan Campers, Unsplash


