Asia
To which language should you translate to localize in Yemen ?
What we know from our community
Yemen’s official language is Modern Standard Arabic, which is the language used in formal contexts like education, books, and news media. However, for day-to-day conversations, the Yemeni colloquial Arabic varieties are used. Each of these varieties are grammatically simplified derivations of the Modern Standard variety, removing many of Arabic’s complex features including the dual-plural form and grammatical case endings. With that said, compared to other Arab majority nations’ colloquial varieties, Yemeni Arabic is conservative, in that it maintains more of the grammatical and phonological features from Modern Standard.
Yemeni Arabic also has several eccentricities, making it challenging for non-Yemenis – even native Arabic speakers – to understand the country’s colloquial varieties. A clear example of this is that Yemeni Arabic is commonly spoken in its own rapid and rhythmic pace, often with the inclusion of unique pronunciation characteristics. Speakers from the south-western governorate of Ibb, for instance, add heavy nasal sounds to their pronunciation of particular letters. Likewise, many Arabic letters are pronounced differently from region to region. Thus, even though words are written the same throughout the country, they will be spoken differently. For instance, the word for “coffee” can be pronounced as qahuah or gahuah, similarly “man” is pronounced as rijal in some areas and riyal in others.
Along with Arabic, Yemen is also home to a handful of other Semitic languages, namely Razhihi, Soqotri, Mehri, Bathari, and Hobyot. These languages are found in small, isolated communities within Yemen. Generally, Yemenis who speak these languages are also bilingual in Yemeni colloquial Arabic.
Arabic
تُعد اللغة العربية الفصحى هي اللغة الرسمية في اليمن، وهي لغة المخاطبات الرسمية والتعليم والكتب والصحافة. ولكن لليمنيين لهجاتهم الخاصة المُستخدمة في المحادثات اليومية. تلك اللهجات تُعد نسخة مبسطة مستمدّة من اللغة العربية الفصحى. ومع ذلك فإن اللهجات اليمنية مازالت أقرب إلى اللغة العربية الفصحى عن غيرها من اللهجات العربية الأخرى لما تحتفظ به من سماتها النحوية والصرفية. تتميز اللهجات اليمنية بإيقاعها السريع، كما تختلف كل منطقة عن الأخرى في طريقة نطق الأصوات. فمثلا يتميز سكان محافظة إب بإضافتهم لصوت الغُنّة في نهايات بعض الكلمات. كذلك يختلف نطق بعض الكلمات بحسب المنطقة، مثل كلمة “قهوة” في بعض المناطق تُنطق “جهوة” أو كلمة “رجّال” تُنطق “ريّال” في بعض المناطق. هذه السمات المميزة والاختلافات في اللهجات اليمنية قد تجعلها صعبة الفهم من قِبل غير اليمنيين من البلاد العربية الأخرى.
بالإضافة إلى اللغة العربية، توجد بعض اللغات السامية الأخرى المُستخدمة في اليمن، كالرازحية، والسقطرية، والمهرية، والبطحرية، والهيبوتية. والتي يستخدمها عدد قليل من سكان اليمن إلى جانب لهجتهم اليمنية العربية.
Somaia, bilingual Arabic analyst II at Legitscript
LANGUAGE INSIGHT
Official language
Arabic (99.6%)
Actual languages
Arabic (99.6%), other (0.4%).
What the top 150 best localized websites in the world do in Yemen
(Top 150 websites listed in the Global by Design ranking – published annually by Byte Level Research, this report provides a list of globally localized websites, showcasing best practices and emerging trends in their globalization)
- 25/150 localize by translating into Arabic
-
3M
-
ABB
-
Accenture
-
Adidas
-
Adobe
-
Airbnb
-
Aldi
-
Amazon
-
American Airlines
-
American Express
-
Apple
-
Audi
-
Autodesk
-
Avis
-
Bayer
-
BMW
-
Booking.com
-
Bosch
-
British Airways
-
Bumble
-
Burberry
-
BYD
-
Canon
-
Capgemini
-
Cartier
-
Caterpillar
-
Chevrolet
-
Cisco Systems
-
Citibank
-
Coca-Cola
-
Costco
-
Dell
-
Deloitte
-
Delta
-
DHL
-
Disney+
-
Dyson
-
eBay
-
Eli Lilly
-
Emirates
-
Ernst & Young
-
Facebook
-
FedEx
-
Ford
-
Four Seasons
-
Fujifilm
-
GE
-
Gillette
-
GoDaddy
-
Google
-
Gucci
-
Haier
-
Heineken
-
Hermès
-
Hertz
-
Hilton
-
Hisense
-
Hitachi
-
Honda
-
Hotels.com
-
HP
-
HP Enterprise
-
HSBC
-
Huawei
-
Hyatt
-
Hyundai
-
IBM
-
IKEA
-
Intel
-
InterContinental Hotels
-
J&J
-
Jack Daniel's
-
Jehovah’s Witnesses
-
John Deere
-
Kellogg's
-
Kia
-
KPMG
-
L'Oréal
-
Land Rover
-
LEGO
-
Lenovo
-
Lexus
-
LG
-
Louis Vuitton
-
Lululemon
-
LUSH
-
Marriott
-
MasterCard
-
McDonald's
-
Mercedes-Benz
-
Merck
-
Microsoft
-
Mitsubishi Electric
-
Nestlé
-
Netflix
-
Nike
-
Nikon
-
Nintendo
-
Nio
-
Nissan
-
NIVEA
-
Oracle
-
Pampers
-
Panasonic
-
PayPal
-
Pepsi
-
Pfizer
-
Philips
-
Pitney Bowes
-
Porsche
-
Procter & Gamble
-
PWC
-
Revolut
-
Rolex
-
Royal Caribbean
-
Salesforce
-
Samsung
-
Sanofi
-
SAP
-
Sephora
-
Shopify
-
Siemens
-
Sony
-
Spotify
-
Starbucks
-
Steelcase
-
Stripe
-
Subaru
-
Tesla
-
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
-
Tiffany
-
Tinder
-
Toshiba
-
Toyota
-
TripAdvisor
-
Uber
-
United Airlines
-
UPS
-
Visa
-
Volkswagen
-
Volvo Cars
-
Vrbo
-
Walmart
-
Western Union
-
Wikipedia
-
Wise
-
WordPress
-
Workday
-
Xerox
-
Xiaomi (Mi)
-
Zara
-
Zoom
If you need others information, below you can find a selection of economic/social/cultural data
Introduction
Language
Official language
Arabic (99.6%)
T-index
0.0097%
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales.
Other languages and dialects
Sanaani, Ta Izzi-Adeni, Hadrami, Gulf and Judeo-Yemen.
The non-Arabic languages of Yemen include Razihi, Soqotri, Mehri, Bathari and Hobyot
Foreign languages
English, Russian
English
Very low proficiency (EF) – 112 of 112 countries/regions in the world- 12/12 position in the middle east.
Demography
Capital: Sana’a
Currency: Yemeni rial
Population: 30,49 m
Population density: 56.49/km2
Economy
GDP: 21.06 billion USD (2021)
GDP per capita: 690.8 USD (2021)
Exports: $1.26 billion (2020)
Statistics
Internet users: 26.7% penetration, 8.24 million
Unemployment rate: 12.81% (2019)
Urbanisation: 34.64% (2018)
Literacy: 49% (2018)
Conventions
Numbering system
Arabic numbering system and comma as decimal separator.
Date format: yyyy-mm-dd / dd-mm-yyyy
Time: 24h time system
Country code: 00967
Language data sources: Worldatlas/Britannica//EF/Wikipedia; Demography data sources: IMF/Worldometers; Conventions data source: Wikipedia; Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal; Statistics data sources: Datareportal/WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF/Culturalatlas/Commisceoglobal
Facts and data
Economy
Imports
$10.5 billion (2020). Wheat ($674M), Rice ($395M), Raw Iron Bars ($363M), Cars ($354M), and Raw Sugar ($342M), importing mostly from China ($2.88B), United Arab Emirates ($1.18B), Saudi Arabia ($1.07B), Turkey ($835M), and India ($791M).
Financial inclusion factors (over 15 years of age)
• 6.4% have an account with a financial institution
• 0.4% have a credit card
• 3.5% have a mobile money account
• 0.7% make online purchases
Ease of doing business
Easy to conduct business (31.8 out of 100) 8th out of 20 North Africa and Middle East countries 187th worldwide out of 190 countries (2019, World Bank).
Exports
$1.26 billion (2020). Crude Petroleum ($682M), Gold ($114M), Non-fillet Frozen Fish ($58.1M), Non-fillet Fresh Fish ($49.4M), and Industrial Fatty Acids, Oils and Alcohols ($31.6M), exporting mostly to China ($597M), Saudi Arabia ($174M), United Arab Emirates ($125M), Malaysia ($61.5M), and Thailand ($43.2M).
Main local online stores
Lazada, The Gioi Di Dong, Sendo, Shopee, Tiki
Global Innovation Index
Ranked 10th out of 17 Northern African and Western Asian countries, 131st out of 132 worldwide.
The Global Innovation Index captures the innovation
ecosystem performance of 132 economies and tracks the most recent global innovation trends.
Economy data sources: WTO/OEC/CIA/Esomar/Datareportal
Service Exports (2015)
Source: OEC
Service Imports (2015)
Source: OEC
Most specialised products by RCA Index
Source: OEC
Most complex products by PCI
Source: OEC
Export Opportunities by Relatedness
Source: OEC

T-index
Reach most of the online purchasing power
T-Index ranks countries according to their potential for online sales. It estimates the market share of each country in relation to global e-commerce.
Try it nowMedia
Media language
Arabic
Information channels
Yemen’s media have been polarised since the power struggle that erupted into open warfare in 2015. TV and radio dominate the media scene. The press, once among the liveliest and most outspoken in the region, has suffered more than other types of media from the effects of conflict. Many publications have folded, or suspended their print editions. The English-language press has all but disappeared. State TV is caught in a tug-of-war between the rebel Houthi movement and the Hadi government. Each side operates its own version of the two main channels, Yemen TV and Aden TV. Private satellite TVs operate from inside Yemen or from abroad, depending on the political climate and their relations with those in power. Journalists work in very difficult circumstances. Reporters Without Borders says reporters have been killed in air raids by the Saudi-led military coalition fighting the Houthis. Other journalists have disappeared; many of them are believed to be detained by the Houthis.
Press
Al-Thawrah – (The Revolution), government-owned daily, under Houthi control
Al-Yaman al-Yawm (Yemen Today) – associated with family of late ex-President Saleh
Sada al-Masirah – Houthi newspaper
Television
Republic of Yemen Television – pro-Houthi and pro-Hadi versions of the state TV are on the air
Yemen Today – private, supported late former president Saleh
Suhayl TV – pro-Islamist, via satellite
Al-Masirah (The March) – Houthi TV, operates from Beirut
Al-Sa’idah (The Happy One) – popular entertainment-based satellite network broadcasting from Egypt
Radio
Republic of Yemen Radio – state-run; Sanaa-based operations are under Houthi control
News Agencies
Yemen News Agency (Saba) – state-run, English-language pages
Marebpress – popular privately-run news site
Al-Tagheer – (Change), privately-run news site
Yemen Portal – news aggregator
Media data source: BBC
Internet Data
Internet users
26.7% penetration, 8.24 million
Share of web traffic by device
80.02% mobile phones, 19.27% computers (laptops and desktops), 0.70% tablet devices,
Median speed of fixed Internet connection
2.76 Mbps
Mobile connection as a percentage of total population 62.2%
Percentage of mobile connections that are broadband (3G-5G) 21.6%
Most popular web search engines
Google (98.39%), Bing (1.06%), Yahoo (0.18%), DuckDuckgo (0.12%), Yandex (0.11%)
Most used social media
Facebook (73.44%), Twitter (7.22%), YouTube (5.53%), Pinterest (6.06%), Instagram (6.19%), Reddit (0.73%), Tumblr (0.28%)
Internet data sources: Datareportal/Statcounter
Social statistics
Life expectancy
66.09 yrs (2017)
Average age of the population
29.2 yrs (2020)
Class & Ethnicity
Yemen is a tribal society; therefore, people are mostly considered according to their tribe/city of origin. Depending on the organisation, where you come from may have a significant influence on where you go within the organisational structure.
Ethnic differences also effect dynamics within the organisational structure, with a “pure” Yemeni, a Yemeni whose both parents are from Yemen, being favoured over the “Muwalad” Yemeni who has a parent from a different country.
Healthcare expenditure
7.5% of GDP (2018)
Religion
Yemenis have a high consideration for religion and religious practices, as evidenced the various breaks for prayer during regular business hours.
Cultural Curiosities
Yemenis are predominantly Muslim, residents however are free to practice whatever religion they prefer. Paradoxically the government denies the conversion of Muslims to other religions and actively prohibits attempts to convert Muslims to other religions.
As in many predominantly Muslim countries, the role of women is still marginal in society.
Social statistics sources: WorldBank/UN/UNESCO/CEIC/IMF
The Data Factbook is a work in progress project. Our community is helping us to fill it up always with new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write your advices at imminent@translated.com
Languages research
Languages and Dialects spoken in Yemen
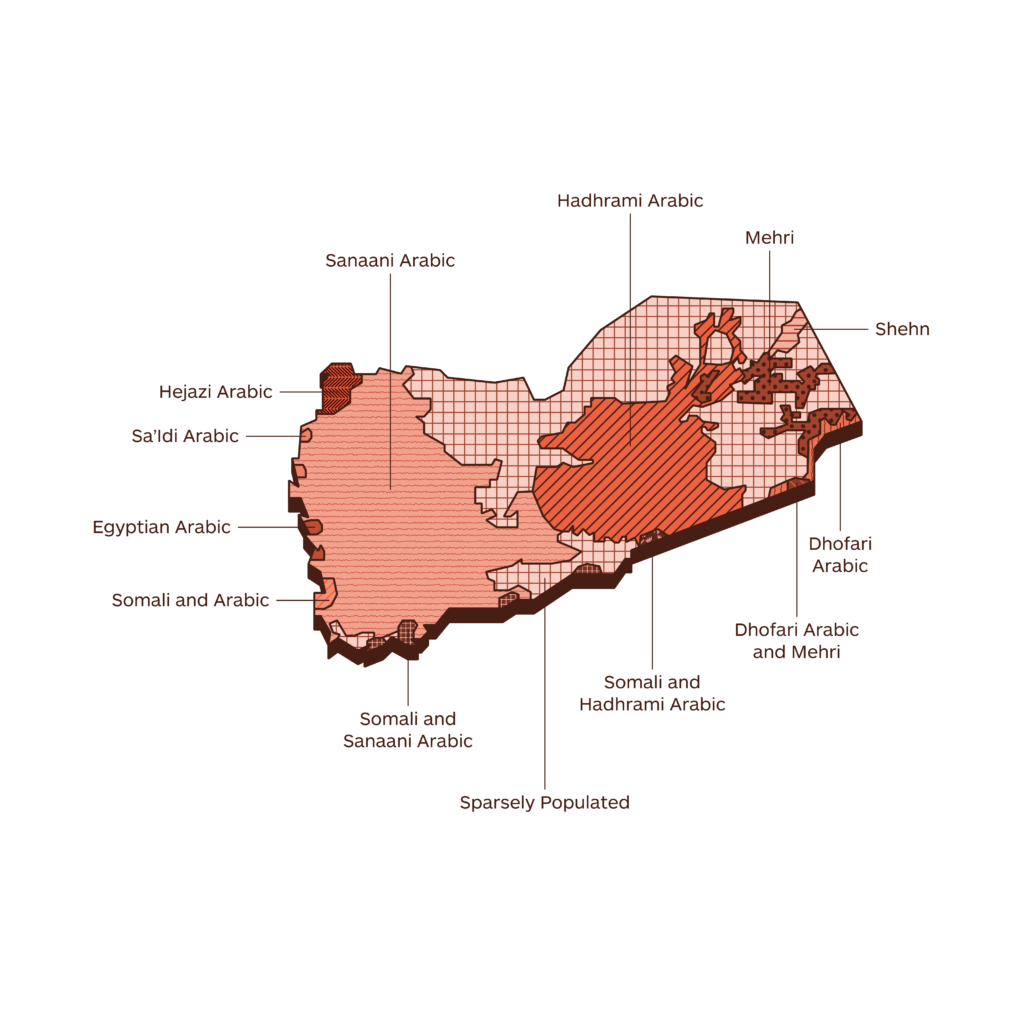
Legend
-
Sanaani Arabic
-
Hadhrami Arabic
-
Mehri
-
Shehn
-
Dhofari Arabic
-
Dhofari Arabic and Mehri
-
Somali and Hadhrami Arabic
-
Sparsely Populated
-
Somali and Sanaani Arabic
-
Somali and Arabic
-
Egyptian Arabic
-
Sa’Idi Arabic
-
Hejazi Arabic
The geographical distribution of languages that you will find in the maps published in this section is a work in progress. Our community is helping us to fill it up with always new and updated data. Your contribution is precious. If you want to help us, please write to imminent.factbook@translated.com
Photo credit: Andrew svk, Unsplash


